Featured
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
What are the Causes of Cracked Heels?
Cracked heels can result from a variety of factors, both external and internal. Understanding these causes is essential for effective prevention and treatment. Some of the primary causes of cracked heels include:
Dry Skin: One of the most joint causes of cracked heels is
excessively dry skin. When the skin on the heels loses its moisture and becomes
dehydrated, it can become brittle and prone to cracking.
Lack of Moisture: Insufficient moisturization of the feet,
especially in dry or cold climates, can lead to dryness and fast of the skin on
the heels.
Dehydration: Inadequate fluid intake can lead to overall
body dehydration, which can, in turn, cause dryness of the skin, including the
heels.
Overexposure to Water: Paradoxically, excessive exposure to
water, specially hot water, can strip the skin of its natural oils, making it
dry and prone to cracking.
Wearing Open-Backed Shoes: Shoes with open backs, such as
sandals or flip-flops, can contribute to the development of cracked heels as
they do not provide adequate support or protection to the heels.
Standing for Long Hours: People who have jobs that want them
to stand for extended periods are at a higher risk of developing cracked heels
because of the constant pressure on their feet.
Obesity: Excess body weight can put extra weight on the fat
pad under the heel, producing it to expand outward and create fissures in the
skin.
Medical Conditions: Certain medical conditions, like
diabetes, eczema, psoriasis, and thyroid disorders, can disrupt the skin's natural
moisture balance and increase the risk of cracked heels.
Aging: As people age, their skin tends to become less
elastic and more prone to dryness, making them more susceptible to developing
cracked heels.
What are Symptoms of Cracked Heels
Cracked heels can range from mild to severe, and the
symptoms may vary accordingly. Common signs and symptoms of cracked heels
include:
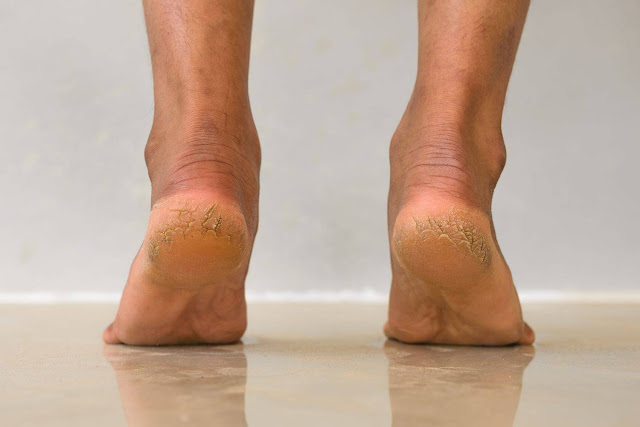
Visible Cracks: The most apparent sign is the presence of
visible, often painful, cracks or fissures on the skin of the heels. These fissures
can be deep and may bleed in severe cases.
Dry, Flaky Skin: The skin on and around the heels may appear
dry, flaky, or rough.
Itching and Redness: The affected area may itch or become
red and inflamed.
Pain or Discomfort: Cracked heels can cause pain and
distress, especially when walking or standing for long periods.
Bleeding: In severe cases, the cracks can lead to bleeding,
increasing the risk of infection.
Thickened Skin: Over time, the skin on the heels may become
thickened as a response to the repeated trauma from walking and pressure.
What are the Risk Factors for Cracked Heels?
Several factors can increase an individual's risk of
developing cracked heels:
Gender: Women are more prone to cracked heels than men due
to differences in skin thickness and hormonal changes.
Age: Older individuals are at higher risk due to naturally
drier and less elastic skin.
Medical Conditions: People with diabetes or skin conditions
like psoriasis and eczema are more susceptible.
Obesity: Excess body weight puts additional pressure on the
feet, increasing the risk of cracks.
Foot Hygiene: Poor foot hygiene and neglecting to moisturize
the feet can contribute to the problem.
Occupation: Jobs that require prolonged standing or walking
can increase the likelihood of developing cracked heels.
Climate: Dry, arid climates and cold weather can exacerbate
dry skin and cracked heels.
Treatment and Prevention
Managing and preventing cracked heels involves a mixture of
lifestyle changes, home remedies, and medical intrusions. Here are some
effective strategies:
Hydration: Stay well-hydrated by intake plenty of water to
keep your skin moisturized from the inside out.
Moisturization: Regularly apply a thick, emollient foot
cream or petroleum jelly to the heels and feet to lock in moisture. For best
results, do this after bathing or before bedtime.
Exfoliation: Gently exfoliate your heels with a pumice pebble or foot file to get rid of dead skin and promote smoother skin.
Proper Footwear: Wear supportive shoes that provide passable
cushioning and protection for the heels. Avoid open-backed shoes that expose
the heels to friction.
Orthotic Inserts: Consider using orthotic inserts or heel
cups to provide additional support and reduce pressure on the heels.
Avoid Hot Water: Use lukewarm water in its place of hot
water when bathing or soaking your feet to prevent excessive drying.
Regular Nail Care: Trim your toenails properly to prevent
them from digging into the skin and causing further damage.
Medical Treatment: In severe cases, consult a healthcare
professional or a podiatrist for professional treatment options. They may
recommend prescription creams, ointments, or therapies like laser treatment.
Manage Underlying Conditions: If you have causal medical
conditions contributing to cracked heels, such as diabetes or eczema, manage
them effectively with the help of a healthcare provider.
Lifestyle Changes: Maintain a healthy diet and exercise
routine to control body weight, as obesity can increase the risk of cracked
heels.
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
Popular Posts
Body Dysmorphia: Types, Causes, and then some
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps


Comments
Post a Comment